Discover how to manage Windows Hello for Business (WHfB) using Intune. Although the process may appear complex, with the right approach, it becomes surprisingly straightforward. We’ll explore different options, making it easy for you to configure WHfB—from device enrollment to post-enrollment methods.
Choosing the Right WHfB Management Method
The world of WHfB management with Intune offers multiple avenues for you to explore:
1. Device Enrollment (Tenant-Wide Policy)
This option targets your entire organization and supports Windows Autopilot. It’s ideal if you wish to enable or disable WHfB for your entire organization with a uniform configuration. The tenant-wide policy applies during device enrollment and covers each user logging in.
Note: You cannot target specific group in this policy.
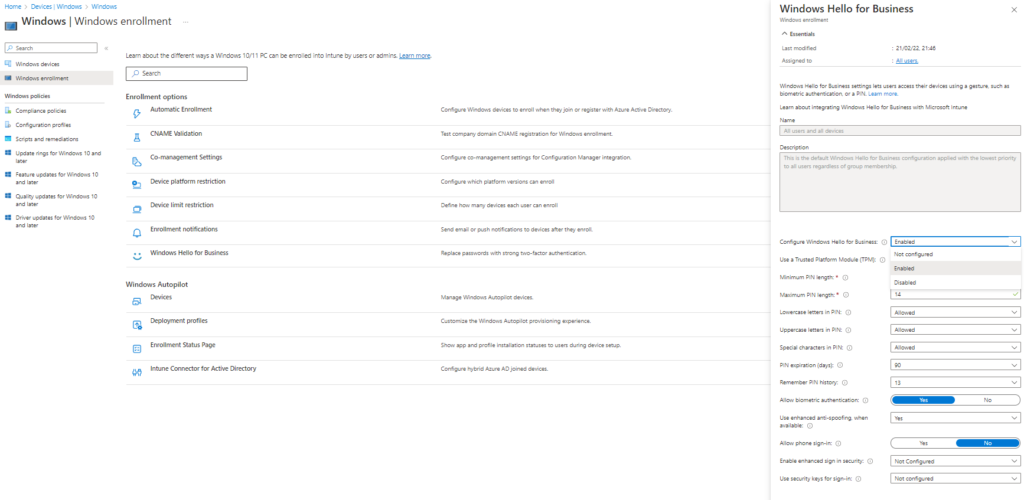
Tenant-Wide Policy Choices:
- Enabled: Configure WHfB settings for the entire organization.
- Disabled: Prohibit WHfB during device enrollment.
- Not configured: Intune doesn’t control WHfB settings.
2. After Device Enrollment:
Assuming you’ve opted for a “Not configured” tenant-wide policy due to varying WHfB configurations needed for different scenarios, here are four Intune methods:
a. Account Protection (Preview):
Found under Endpoint Security, this method offers a well-structured interface for configuring WHfB policies.
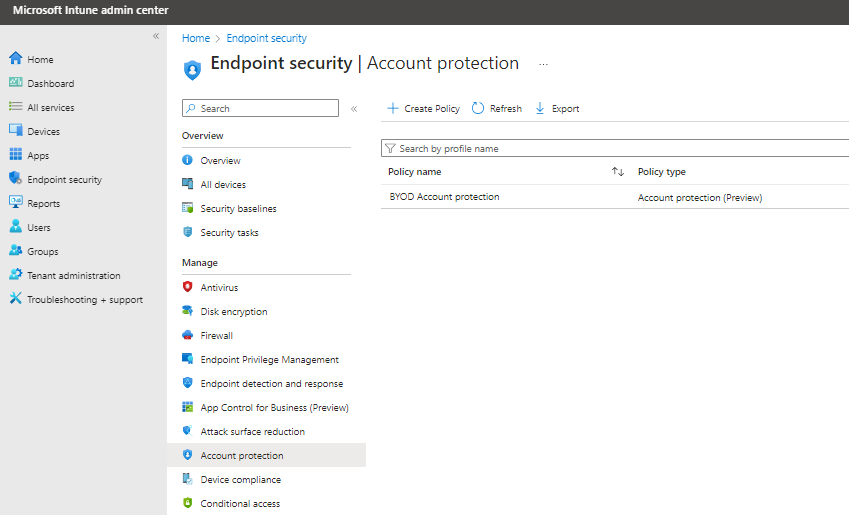
How It Works:
- Device Group Assignment: Prompts all users to configure WHfB during their first logon.
- User Group Assignment: Targeted users receive the WHfB prompt after WHfB policy syncs.
Considering Device vs. User Configurations:
For consistent settings across users’ devices, use device configuration deployed to a device group. However, if you need user-specific settings, opt for WHfB user configurations. Note that certain settings are accessible only through device configuration.

